
NEO-3DF: Novel Editing-Oriented 3D Face Creation and Reconstruction
ACCV 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
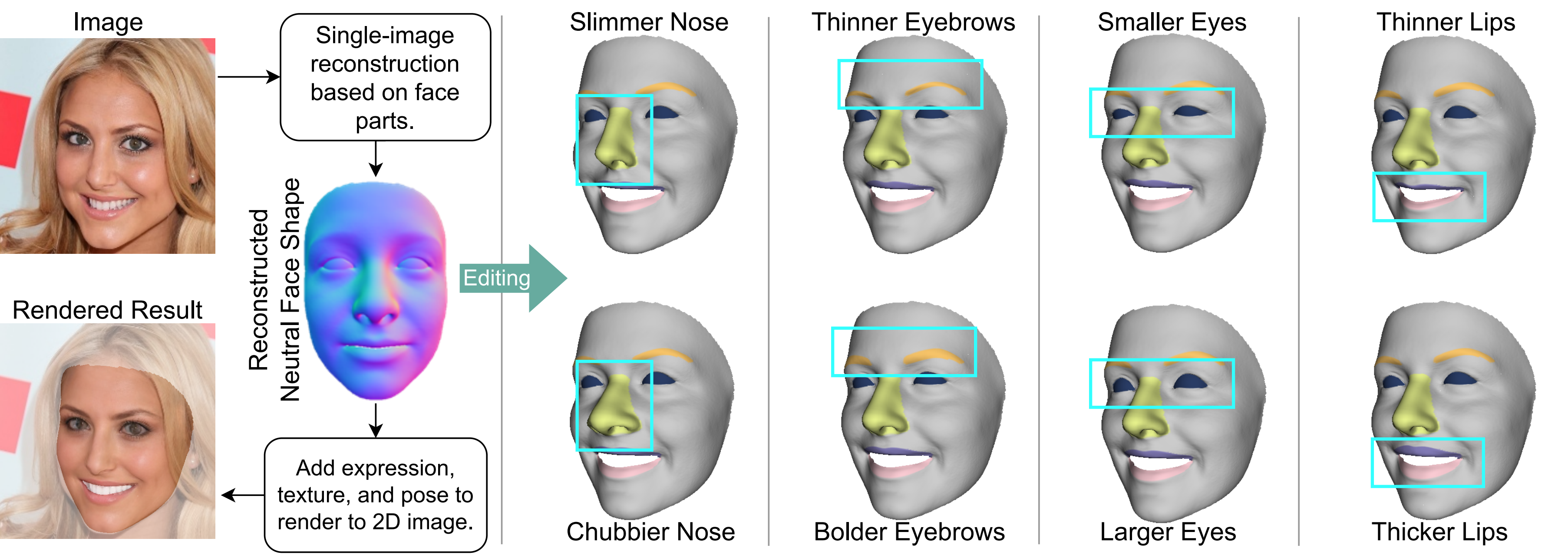
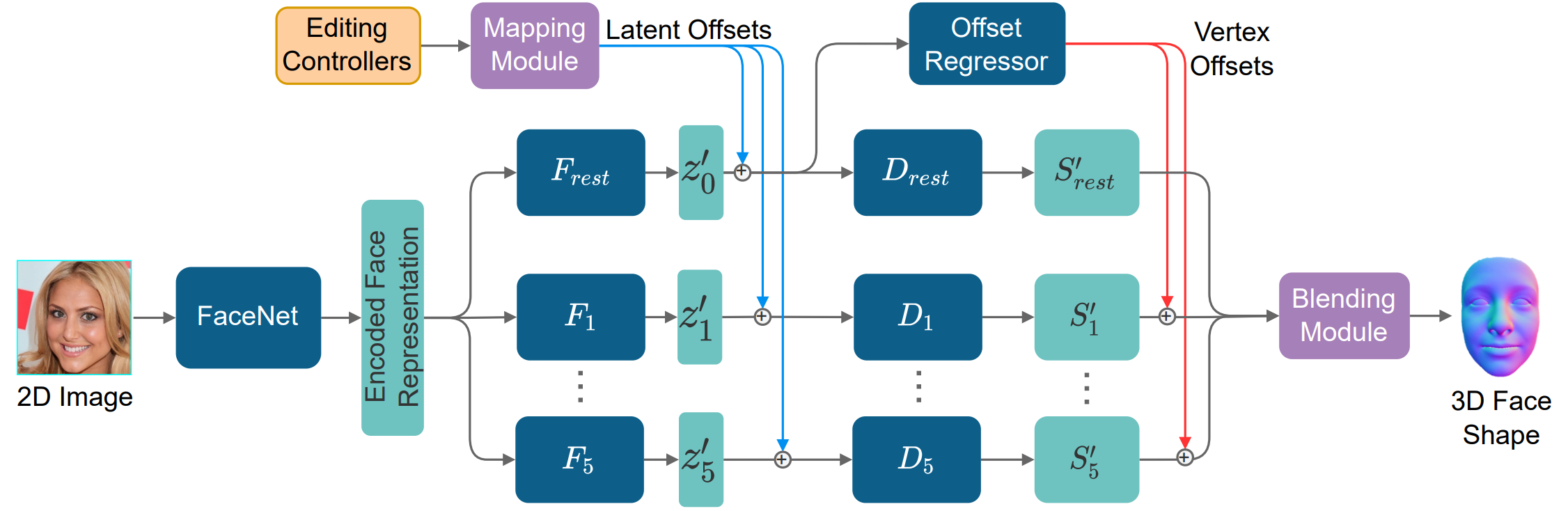
| Unlike 2D face images, obtaining a 3D face is not easy. Existing methods, therefore, create a 3D face from a 2D face image (3D face reconstruction). A user might wish to edit the reconstructed 3D face, but 3D face editing has seldom been studied. This paper presents such method and shows that reconstruction and editing can help each other. In the presented framework named NEO-3DF, the 3D face model we propose has independent sub-models corresponding to semantic face parts. It allows us to achieve both local intuitive editing and better 3D-to-2D alignment. Each face part in our model has a set of controllers designed to allow users to edit the corresponding features (e.g., nose height). In addition, we propose a differentiable module for blending the face parts and making it possible to automatically adjust the face parts (both the shapes and the locations) so that they are better aligned with the original 2D image. Experiments show that the results of NEO-3DF outperform existing methods in intuitive face editing and have better 3D-to-2D alignment accuracy (14\% higher IoU) than global face model-based reconstruction. |
 |
 |
Yan, P., Gregson, J., Tang, Q., Ward, R., Xu, Z., & Du, S. NEO-3DF In ACCV, 2022. |
[Supplementary Material] |
Acknowledgements |